
2. 執行「開始—執行—cmd」,預設會在這個資料夾:
C:\Documents and Settings\%HOME%>
3. 切換目錄至「.android/avd/DAVID_2.2」,指令參考如下:
C:\Documents and Settings\David.Lanz>cd .android
C:\Documents and Settings\David.Lanz\.android>cd avd
C:\Documents and Settings\David.Lanz\.android\avd>cd DAVID_2.2.avd
畫面結果:
C:\Documents and Settings\David.Lanz\.android\avd\DAVID_2.2.avd>

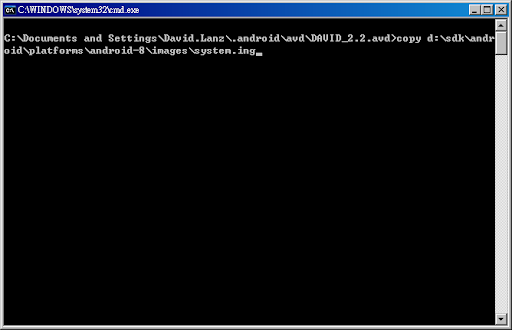
4.複製SDK裡的system.img至此,指令如下:
copy d:\sdk\android\platforms\android-8\images\system.ing
5.在DOS視窗中切換目錄至SDK的tools資料夾,手動啟動模擬器,指令:
cd d:\sdk\android\tools\
emulator -avd DAVID_2.2 -partition-size 96

順利執行模擬器畫面

6.在DOS視窗裡執行指令,取出build.prop檔案。
adb pull /system/build.prop

7.利用文字編輯器開啟編輯build.prop這個檔案,將 ro.config.nocheckin=yes 移除(再最前面加上 mark 符號 #)

8.將剛才取出修改好的檔案存檔,然後執行以下指令將檔案放回去。
adb remount
adb push build.prop /system

9.至此下載Froyo用的Market程式,將之解壓縮後,存放至SDK資料夾(舉例如下):
D:\SDK\android\tools\GoogleServicesFramework.apk
D:\SDK\android\tools\Vending.apk
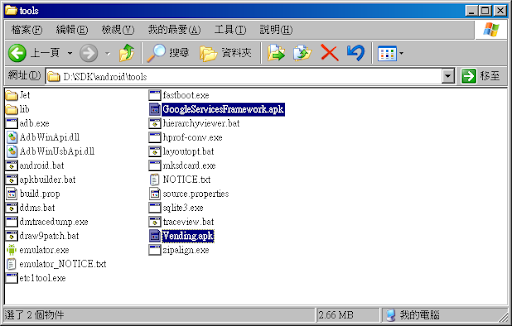
10.將步驟9的兩個apk檔案丟入模擬器/system/app資料夾,並刪除SdkSetup.apk,指令如下:
adb push GoogleServicesFramework.apk /system/app
adb push Vending.apk /system/app
adb shell rm /system/app/SdkSetup.apk

11.關閉 Emulator(直接關閉模擬器的視窗即可)。
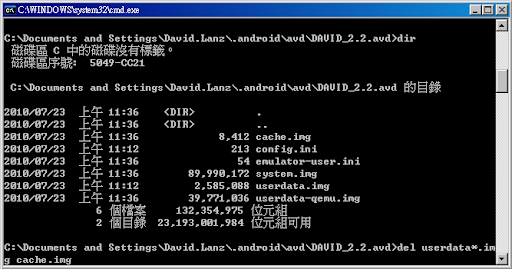
12.切換目錄至avd的資料夾下:
C:\Documents and Settings\%HOME%\.android\avd\DAVID_2.2.avd>
執行以下指令,刪除由系統產生的「userdata-qemu.img」與「userdata.img」、「cache.img 」這三個檔案刪除,讓Emulator完成初始化。
del userdata*.img cache.img
13.執行「Android SDK and AVD Manager」來啟動模擬器。



大功告成,Market順利在模擬器裡執行。第一次執行Market必須要以google帳號登入,登入後即可下載程式囉。



I can install the market, but I can't install App from it. Maybe someone can help me.